Holding a newborn baby

All of us love to cuddle and hold a baby .But most of us are sceptical of how to hold a small baby. Below are some of the steps that can make newborn handling much easier and safer viz:
Step 1: Wash your hands-Always make sure your hands are clean before you pick up your baby. Baby’s immune system is still developing, so any germs you carry may make them sick. While lathering with soap and warm water works well, consider keeping hand sanitizer around for guests who also want to cuddle your little one. Clean your hands each time before holding your baby.
Step 2: Get comfortable-Comfort is one of the most important things about holding your baby. Not only do you want to feel physically comfortable, but you also want to feel confident in your hold.
Step 3: Provide support-When holding a newborn, it’s very important to always have a hand to support the head and neck. After all, your baby’s head is the heaviest part of their body at birth. Pay special attention to baby’s fontanelles, which are the soft spots on the top of their head.
Newborns lack the critical neck muscle control to keep their heads supported on their own. This milestone isn’t usually reached until closer to FOUR months.
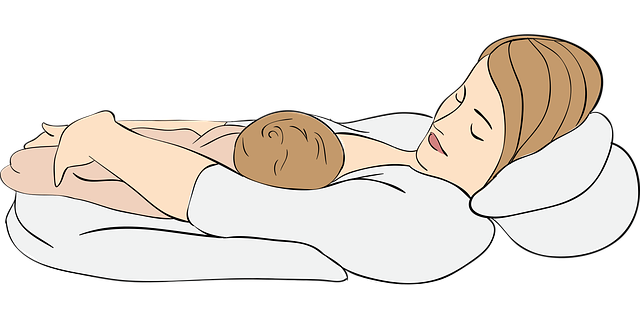
Step 4: Choose your position-Holding starts with picking baby up. When you go to lift your baby, place one hand under their head and another under their bottom. From there, raise their body to your chest level. As long as you’re supporting baby’s head and neck, the position is up to you. There are a variety of holds you and your baby might enjoy. Some of these positions are also great for breast-feeding or burping. Various positions are as follows viz
Cradle Hold
The cradle hold is one of the easiest and best ways to hold your newborn for the first several weeks of life:
- With your baby horizontal at your chest level, slide your hand from their bottom up to support their neck.
- Gently nudge baby’s head into the crook of your elbow.
- While still cradling their head, move your hand from the supporting arm to their bottom.
- Your free arm will be able to do other things or provide extra support.
Shoulder hold
- With baby’s body parallel with your own, lift their head to shoulder height.
- Rest their head on your chest and shoulder so they can look out behind you.
- Keep one hand on their head and neck, and your other supporting baby’s bottom. This position may also allow baby to hear your heartbeat.
Belly hold
- Lay your baby, stomach down, across your forearm with the head up toward your elbow.
- Their feet should land on either side of your hand, angled closer to the ground so the baby is at a slight angle.
- This position is helpful if baby is gassy and needs to be burped. Gently stroke baby’s back to work out the gas.
Lap hold
- Sit in a chair with your feet firmly on the ground and place your baby in your lap. Their head should be at your knees, face up.
- Lift their head up with both of your hands for support and your forearms under their body. Baby’s feet should be tucked in at your waist
Do’s:
- Try skin-to-skin contact while holding baby. It’s a great way to bond and keep them warm. You can strip baby down to their diaper, place them against your bare chest, and cover with a blanket.
- Choose a seated position if you feel nervous about holding baby. Sitting down is also a good idea for anyone who might not have the strength to support baby’s weight, like children and older individuals.
- Use a baby carrier for hands-free holding. Follow all instructions on the carrier’s packaging. It suggests age-appropriate holds and positions.
- Use an infant support pillow, when holding baby for extended periods of time or to help with breast-feeding.
- Hold your baby with both hands while you’re going up and down the stairs for added safety.
Dont’s
- Do not cook or carry hot drinks while holding baby. Knives, flames, and excess heat are dangerous and could lead to injury by accident. Stay away from others who are working with those things near you.
- Do not ever shake your baby, whether to play or to express frustration. Doing so can cause bleeding in the brain and even death.
To read more on Baby care, click on the link below,
New-Born