Hot or Cold Compress for Injuries
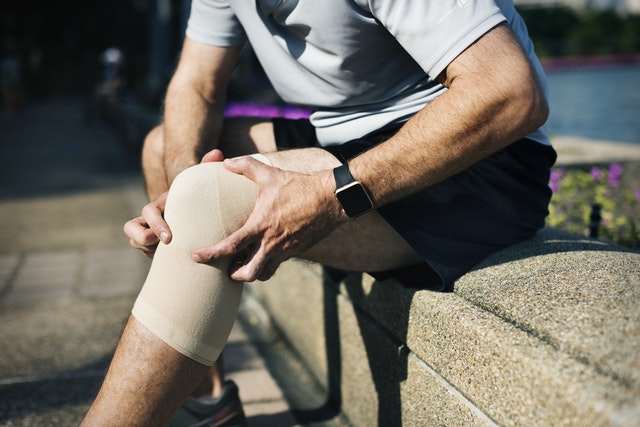

There is so much confusion about this issue because therapeutic icing and heating — cryotherapy and thermotherapy — are rational, cheap, easy, safe self-treatment options for many common painful problems.
Ice is for fresh injuries, and heat is for stiff, aching muscles.
Ice is for injuries — calming down damaged superficial tissues that are inflamed, red, hot, swollen, pain or if it is bleeding/ post surgical pain. The inflammatory process is a healthy, normal, natural process; that also happens to be incredibly painful and more biologically stubborn than it needs to be. Icing is mostly just a mild, drugless way of dulling the pain of inflammation and taking swelling down a bit. Examples: a freshly pulled muscle.
Heat is for muscles, chronic pain, and stress — taking the edge off symptoms like muscle aching and stiffness, which have many unclear causes, but trigger points are probably one of the usual suspects. Chronic pain, especially back pain, often involves lots of tension, anxiety, hyper vigilance, and sensitization, and comfortable heat can soothe a jangled mind and nervous system. Stress and fear are major factors in many painful problems, of course.
Alternating between applications of ice and heat is called contrasting therapy. It’s extremely stimulating and is mostly used to facilitate injury recovery, with unknown efficacy.
What ice and heat are not for
Both ice and heat have the potential to do some minor, temporary harm when used poorly. Heat can make inflammation significantly worse. Ice can aggravate symptoms of tightness and stiffness; it can also just make any pain worse when it’s unwanted.
Both ice and heat are pointless or worse when unwanted: icing when you’re already shivering, or heating when you’re already sweating. The brain may interpret an excess of either one as a threat, but icing is more threatening and when brains think there’s a threat, they may also amp up the pain. Ice seems to be feel more threatening to most people.
Trigger points (painfully sensitive spots) can be surprisingly intense and easily mistaken for “iceable” injury and inflammation. But if you ice trigger points, they may burn and ache even more acutely. This mistake is made particularly often with low back pain and neck pain — the very conditions people often try to treat with ice.
Heat and inflammation are the other particularly bad combination.
How to use Ice
After an acute injury, such as an ankle sprain, or after activities that aggravate a chronic injury, such as shin splints.
Use an ice bag with cubed ice, ice pack or ice massage. When using an ice pack that does not have real ice cubes,use a thin towel between the ice pack and the skin to prevent frostbite.
Do not use ice longer than 20 minutes at a time. More time spent icing does not mean more relief. Be sure the area goes numb, then make sure the skin returns completely back to normal before reapplying.
How to apply heat
Before activities that aggravate chronic injuries, such as muscle strains. Heat can help loosen tissues and relax injured areas.
Apply heat using a heating pad or a hot wet towel.
No more than 20 minutes at a time. Never apply heat while sleeping. Be careful not to burn yourself.
To read more on First Aid, click on the link below.